PAT.Identity+Permission Management

|
PAT | Identity & Permission Management | Version: | 0.4 | 
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Document type: | Pattern Type | Owner: |

Description
This Pattern Type belongs to "Infrastructure Sector Operations". This facility handles the tasks associated with maintaining more than one identity store and/or more than one permission register within the organization. It can collect accounts from source systems, and provision them to target stores/registers. Ideally, there is only ONE Identity & Permission Management facility in the organization, connected to all Identity Stores and all Permission Registers. The facility is dependent on a metadirectory (aggegating all identities in a single Identity Store), a virtual directory (offering an aggregated view on all Identity Stores combined), or a comprehensive and complete information model for all identities and associated attributes in the organization.
Identity management
This facility has the following identity-related tasks:
- To create new identities in Identity Stores when the circumstances call for it (either an eligible new identity presents itself, or an existing identity becomes eligible), including all identity attributes for that Identity Store;
- If an identity attribute changes in an identity store that is deemed authoritative for that particular attribute, then update this attribute in all serviced Identity Stores where that same identity appears AND that attribute is present;
- As soon as an identity's eligibility for an account in a particular Identity Store ends, disable or remove the identity from that identity store;
- To resolve conflicting information in different Identity Stores when it is discovered.
Permission management
This facility has the following permission-related tasks:
- If an identity becomes eligible for access to certain resources, create permissions in the Permission Register(s) associated with these resources;
- If an identity loses eligibility for access to certain resources, remove the permissions present in the Permission Register(s) associated with these resources;
- To resolve conflicts between specific permissions assigned to an identity in a Permission Register (or not) and the permissions actually granted to it (or not).
Details
The facility allows for the following:
- It monitors at least all Identity Stores that have one or more authoritative attributes. Monitoring can be performed actively or passively. Actively means the facility periodically polls the Identity Stores to see if there are relevant changes; passively means the facility waits for a signal from the Identity Store itself that a change has occurred.
Note that the depiction of an identity store and permission register in the drawing below is only indicative: the Identity & Permission Management pattern looks after identity stores and permission registers, but in itself isn't one of either.
Graphical Overview
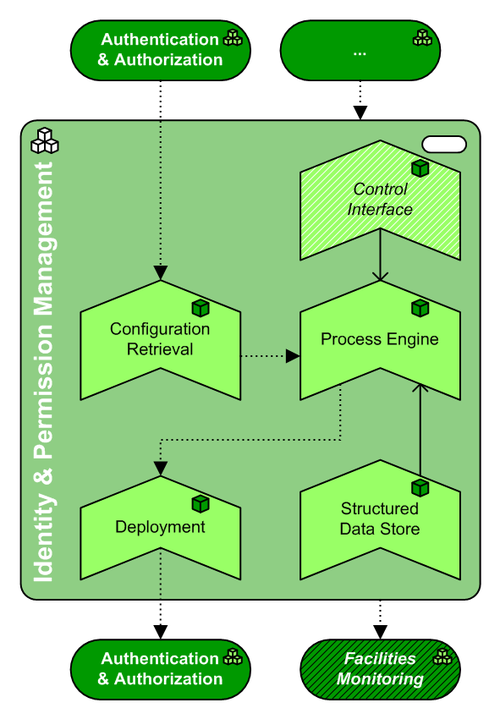
This is the graphical representation of the infrastructure functions in this Pattern Type, plus their main relations:

(The source file of this picture can be downloaded here).
Pattern Type Composition
This pattern has the following mandatory and optional subfunctions, expressed in Building Block Types:
| Icon | Function | WA | Inclusion | Rationale |
| Process Engine | SE | mandatory | This is the engine that processes new or changed identities and/or permissions. It is probably rule-based, and can source authoritative identity attributes and permissions from multiple identity stores and permission registers. Furthermore, it hands off new or changed identity (attributes) and/or permissions to the Deployment facility for replication over a multitude of identity stores and permission registers. | |
| Control Interface | SE | optional | A "self-help" interface can be provided to the users that have one or more identities in the organisation's IT infrastructure, in order to change/reset their passwords, update identity attributes directly in the system et cetera. Note that the nature of this interface is such, that most anyone can access it. Checks for the actual identity of a user of this interface should take sufficient precautions against unauthorized use, to prevent security breaches. | |
| Deployment | SS | mandatory | This facility can push the new or changed identity (attributes) and/or permissions to other identity stores and permission registers. | |
| Configuration Retrieval | SS | mandatory | The Process Engine needs a means to interrogate all Identity Stores and Permission Registers that receive data and/or supply (authoritative) data. Hence this facility serves to model this means. Interrogation can occur on external triggers (a change in a monitored Store/Register), on schedule, or on another internal trigger. | |
| Structured Data Store | MW | mandatory | The Process Engine needs a means to coordinate its action, remember the state of the identities/permissions it has distributed over the organization; the Structured Data Store provides this means. Ideally this is a metadirectory combining the authoritative data of all appointed identity stores and permission registers (although it's most likely unwanted to have any facility call upon this metadirectory). If not a metadirectory, then still some sort of scorecard needs to be kept to prevent the facility from unnecessarily provision accounts, or missing out on updated accounts. |
Pattern Type Neighbors
This pattern has the following mandatory and optional relations with adjacent (sub)functions, expressed in Pattern Types (PAT). Note: if the table below is empty, then there are no architecturally prescribed relations with adjacent subfunctions:
| Function | Adjacency | Description |
| Facilities Monitoring | mandatory | The facility is managed by means of this Security Management & Auditing pattern, plus it delivers information to this pattern on existing identities and effective permissions, on changes thereof, and audit information on the company officials and processes that make these changes. |
| Authentication & Authorization | mandatory | Multiple instances of this pattern serve both as sources of permission and/or identity information, and as targets for them. Note that the Identity & Permission Management pattern reads from, and/or writes to, the Identity Store and Permission Register BBTs within each A&A pattern. |
Pattern Variants based on this type
No Patterns Variants implement this Type (yet)