Pattern Type
A Pattern is a set of Building Blocks that form an infrastructure Product/Solution. A Pattern describes the architecture of a solution, being technology and organization agnostic. One ore more Pattern Types serve as archetypes for the modelling of a Pattern Variant, that outlines a solution at implementation level. It houses the general description of the intended functionality of the Pattern Variants based upon it. The full set of Pattern Types form the universal and basic structure of all Infrastructure Landscapes. A clickable map of the Pattern Types that together form the archetype of the Infrastructure Landscape is depicted below:
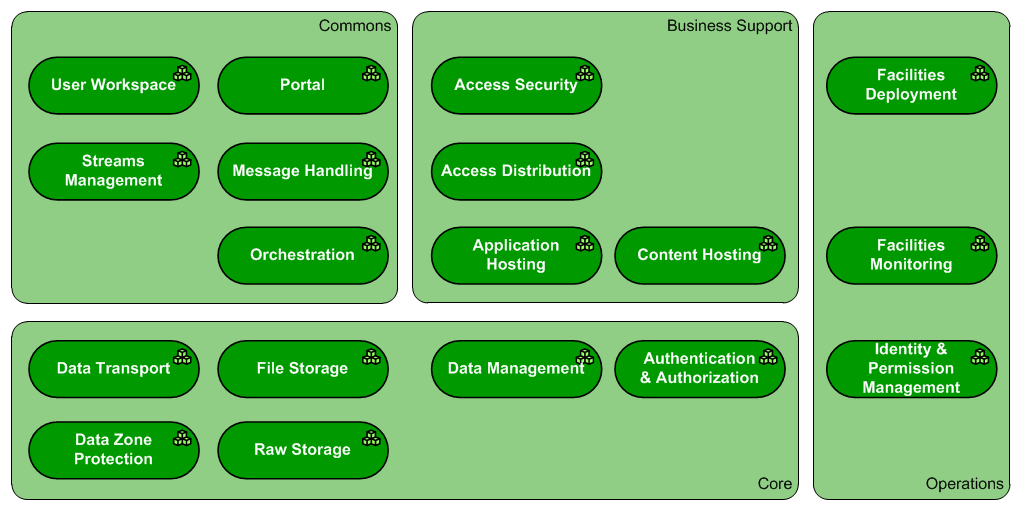
17 Pattern Types are defined in this wiki, excluding 0 PATs under consideration, and 0 obsoleted PATs. Click on the Pattern Type names in the table below to access the Pattern Type descriptions/definitions and the Building Block Types they are composed of:
| Pattern Type | Function | Mandatory BBTs | Optional BBTs | Sector | Maturity |
| Access Distribution | Provides smart access to back-end facilities, providing services such as caching, health/capacity based load balancing etc. | J.A.H. Schoonderbeek | 3 | ||
| Access Security | Controls and secures (external) user connections with back-end facilities and applications | J.A.H. Schoonderbeek | 3 | ||
| Application Hosting | Accommodates (business) applications and services | ?S.A.D. Jumelet? | 3 | ||
| Content Hosting | Hosts content and makes it available in a suitable form(s) to users | J.A.H. Schoonderbeek | 3 | ||
| Streams Management | A generic pattern to send out and/or receive data in time-dependent streams, such as audio, video or gaming information | J.A.H. Schoonderbeek | 3 | ||
| Message Handling | Provides transport, storage and delivery of messages | S.A.D. Jumelet | 3 | ||
| Orchestration | Provides facilities to create, execute and control automated (business/application) workflows | S.A.D. Jumelet | 2 | ||
| User Workspace | Comprises a set of facilities that offer a digital workspace to end-users, that enables them to use and access applications and/or communicate with other end-users | S.A.D. Jumelet | 3 | ||
| Authentication & Authorization | Secures usage of facilities and applications by validating identities and permissions | J.A.H. Schoonderbeek | 3 | ||
| Data Management | Provides preservation, retrieval, manipulation and management of strictly structured data, such as databases | ?J.A.H. Schoonderbeek? | 3 | ||
| Data Transport | Comprises a set of facilities to transport data between automated systems | J.A.H. Schoonderbeek | 2 | ||
| Data Zone Protection | Controls and secures data exchange between two data transport zones | J.A.H. Schoonderbeek | 3 | ||
| File Storage | Carries out the storage and retrieval of loosely structured data at a single, logical location; can provide advanced functionality ("intelligence") to administrators and/or users. | J.A.H. Schoonderbeek | 4 | ||
| Raw Storage | Carries out the storage and retrieval of "raw bits" data at a single, logical location; optionally provides advanced functionality ("intelligence") to administrators and/or users. | J.A.H. Schoonderbeek | 4 | ||
| Facilities Deployment | Provides a set of facilities to automate the deployment and administration of platforms, applications and/or configurations | S.A.D. Jumelet | 3 | ||
| Facilities Monitoring | Comprises a set of facilities to enable centralized and intelligent monitoring of automated systems, either or both for system health care and security purposes | S.A.D. Jumelet | 3 | ||
| Identity & Permission Management | Provides consistent deployment and management of identity stores and/or permission registers | J.A.H. Schoonderbeek | 3 |
Note: the following 0 Pattern Types have been proposed.
| Pattern Type | Function | Mandatory BBTs | Optional BBTs | Sector | Maturity |
Note: the following 0 Pattern Types have been obsoleted.
| Pattern Type | Function | Mandatory BBTs | Optional BBTs | Sector | Maturity |