PD.Relational Data Management: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (24 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Maturity|0}} | {{Maturity|0 | ||
|maturity=0 | |||
}} | |||
{{Pageheaderbox4PD | {{Pageheaderbox4PD | ||
|name=Relational Data Management | |name=Relational Data Management | ||
| Line 5: | Line 7: | ||
|version=0.3 | |version=0.3 | ||
|owner=Daniel Jumelet | |owner=Daniel Jumelet | ||
|summary=This Pattern provides the | |summary=This Pattern provides the function layout to model "strictly structured data" handling, in a relational fashion. | ||
}} | }} | ||
This Pattern provides the | This Pattern provides the function layout to model [[OIAm data view|"strictly structured data"]] handling, i.e. it controls the creation, updating and querying of sets of organized data. It is called 'relational data management', because a schema is used to store data in a predefined way, with predefined relations between data objects. The provisioning of the following elements is important with this kind of data handling: | ||
* a "modeling language", to define schemas; | * a "modeling language", to define schemas; | ||
* a "query language", to enable data object reading, creating, updating, and deleting; | * a "query language", to enable data object reading, creating, updating, and deleting; | ||
* a "transaction mechanism", to enable interaction with other (instances of) data management facilities and applications. | * a "transaction mechanism", to enable interaction with other (instances of) data management facilities and applications. | ||
These elements are provided by the [[DOT.Data|Data]][[FD.Engine|Engine]]. Data objects are stored using a predefined (structured) [[DOT.Data|Data]][[FD.Store|Store]]. Both functions form the core of this Pattern. | These elements are provided by the [[DOT.Data|Data]] [[FD.Engine|Engine]]. Data objects are stored using a predefined (structured) [[DOT.Data|Data]] [[FD.Store|Store]]. Both functions form the core of this Pattern. | ||
{{Pattern Realizes | {{Pattern Realizes | ||
|service=SD.Application Database | |service=SD.Application Database | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Pattern Graphic | {{Pattern Definition Graphic | ||
|graphic=PD.Data Management.png | |graphic=PD.Relational Data Management.png | ||
|size=800px | |||
|size= | |||
|title=Relational Data Management pattern | |title=Relational Data Management pattern | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{ | {{Pattern Definition Composition | ||
{{ | |Row_dataobjectype=DOT.Traffic | ||
|function= | }} | ||
{{Pattern Definition Composition Row | |||
|function=FD.Engine | |||
|dataobjecttype=DOT.Data | |||
|choice=Must | |choice=Must | ||
|reason=The Data Engine is the heart of the pattern, as it offers the intelligence to | |reason=The Data Engine is the heart of the pattern, as it offers the intelligence to control strictly structured data handling. | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{ | {{Pattern Definition Composition Row | ||
|function= | |function=FD.Store | ||
|dataobjecttype=DOT.Table | |||
|choice=Must | |choice=Must | ||
|reason=This | |reason=The Table Store offers the predefined storage structure. This is one of the key characteristics of relational data management. | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{ | {{Pattern Definition Composition Row | ||
|function= | |function=FD.Logging | ||
|dataobjecttype=DOT.Transaction | |||
|choice=Must | |choice=Must | ||
|reason= | |reason=Keeping a record of transactions, in order to be able to analyze database interaction and to revert and replay transactions. | ||
}} | |||
{{Pattern Definition Composition Row | |||
|function=FD.Archive | |||
|dataobjecttype=DOT.Log | |||
|choice=May | |||
|reason=Preservation of transaction logs, in order to be able to get further back in time regarding transactions. | |||
}} | |||
{{Pattern Definition Composition Row | |||
|function=FD.Encryption | |||
|dataobjecttype=DOT.Traffic | |||
|choice=May | |||
|reason=When data is exchanged over unsecured data transport facilities, it might be a good measure to encrypt the data at engine level. | |||
}} | }} | ||
{{ | {{Pattern Definition Composition Row | ||
|function= | |function=FD.Caching | ||
|dataobjecttype=DOT.Transaction | |||
|choice=May | |choice=May | ||
|reason= | |reason=Retaining and keeping available of frequent issued transactions/queries, in order to improve performance. | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{ | {{Pattern Definition Composition Row | ||
{{Pattern | |function=FD.Replication | ||
{{ | |dataobjecttype=DOT.Transaction | ||
| | |choice=May | ||
|choice= | |reason=Multiplying transactions over multiple database instances, to maintain exact copies on data engine level. Mostly this is done to create a higher availability | ||
|reason= | }} | ||
{{Pattern Definition Composition Row | |||
|function=FD.Replication | |||
|dataobjecttype=DOT.Table | |||
|choice=May | |||
|reason=Multiplying tables over multiple database instances, to create an exact copy of a database on data engine level. This can be done to create a new development/test environment or to start creating a higher availability | |||
}} | |||
{{Pattern Definition Composition Row | |||
|function=FD.Export | |||
|dataobjecttype=DOT.File | |||
|choice=May | |||
|reason=Extraction of data from the database and putting this in a file. This is used to execute a bulk data transfer from one instance to another. It can be used to create a replica or to import a dataset from one database into the other (ETL). Because it does not require a connection between Data Engines, it offers more flexibility and security, compared to direct Data Engine interaction. In both cases, the proper interfaces should be available. | |||
}} | |||
{{Pattern Definition Composition Row | |||
|function=FD.Import | |||
|dataobjecttype=DOT.File | |||
|choice=May | |||
|reason=Loading of data from a file, to store this data in a database. This is used to restore a database from a replica or to import a large dataset from another database (ETL). Because it does not require a connection between Data Engines, it offers more flexibility and security, compared to direct Data Engine interaction. In both cases, the proper interfaces should be available. | |||
}} | }} | ||
{{ | {{Pattern Definition Composition Row | ||
| | |function=FD.Concealment | ||
|dataobjecttype=DOT.Data | |||
|choice=May | |choice=May | ||
|reason= | |reason=Hiding of (privacy-sensitive) data objects when presenting/transferring/exporting data, by means of masking or scrambling. | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{ | {{Pattern Definition Composition Row | ||
| | |function=FD.Tiering | ||
|dataobjecttype=DOT.Table | |||
|choice=May | |choice=May | ||
|reason= | |reason=Making use of different storage tiers for table retention, to reduce costs. | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{ | {{Pattern Definition Composition Row | ||
| | |function=FD.Encryption | ||
|dataobjecttype=DOT.Table | |||
|choice=May | |choice=May | ||
|reason= | |reason=Encrypting (making unreadable without a key) of data when stored in a structured data store. | ||
}} | |||
{{Pattern Definition Composition Row | |||
|function=FD.Controlling | |||
|dataobjecttype=DOT.Platform | |||
|choice=Must | |||
|reason=Administrative interface to configure and manage database systems. | |||
}} | |||
{{Pattern Definition Composition Row | |||
|function=FD.Logging | |||
|dataobjecttype=DOT.Platform | |||
|choice=Must | |||
|reason=Keeping track of events, activities, interactions that occur during database system operation. | |||
}} | }} | ||
{{Table Ending}} | {{Table Ending}} | ||
Latest revision as of 19:35, 27 November 2019
| Page maturity This page has maturity level 0 (proposal) |
| PD | Relational Data Management | Version: | 0.3 | 
| |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Document type: | Pattern Definition | Owner: |
| This Pattern provides the function layout to model "strictly structured data" handling, in a relational fashion. |
Description
This Pattern Definition serves the creation of models in the Service Category "Data Management". This Pattern provides the function layout to model "strictly structured data" handling, i.e. it controls the creation, updating and querying of sets of organized data. It is called 'relational data management', because a schema is used to store data in a predefined way, with predefined relations between data objects. The provisioning of the following elements is important with this kind of data handling:
- a "modeling language", to define schemas;
- a "query language", to enable data object reading, creating, updating, and deleting;
- a "transaction mechanism", to enable interaction with other (instances of) data management facilities and applications.
These elements are provided by the Data Engine. Data objects are stored using a predefined (structured) Data Store. Both functions form the core of this Pattern.
Services realized
This Pattern realizes the following service(s):
- Application Database (This service provides a data store for applications with a predefined structure)
Functional and Integration view
This is the graphic representation of the function model of this Pattern Definition:
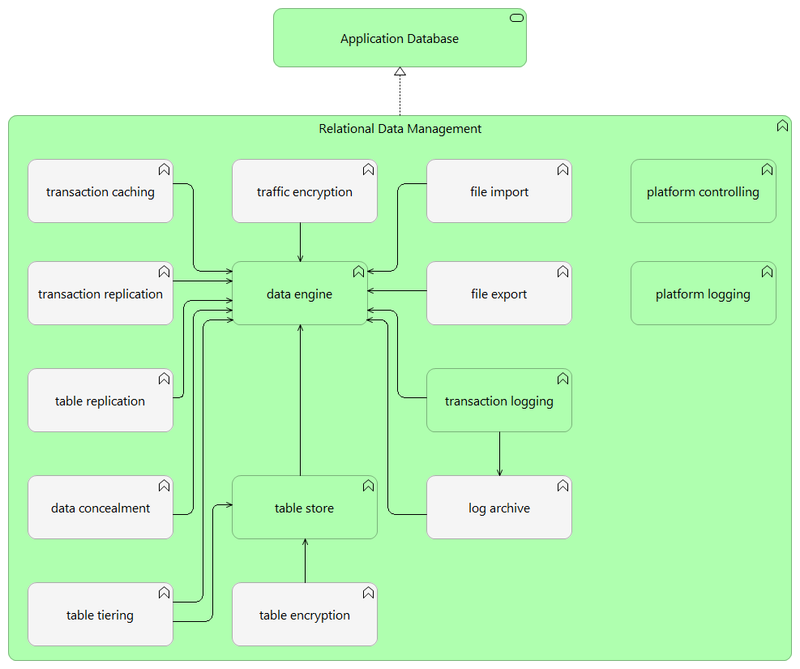
Pattern Definition Composition
This pattern is an aggregation of the following (mandatory and optional) functions, expressed in Data/Object Types and Fundtion Definitions:
| Function | Inclusion | Description/Rationale |
| Data Engine | recommended | The Data Engine is the heart of the pattern, as it offers the intelligence to control strictly structured data handling. |
| Table Store | recommended | The Table Store offers the predefined storage structure. This is one of the key characteristics of relational data management. |
| Transaction Logging | recommended | Keeping a record of transactions, in order to be able to analyze database interaction and to revert and replay transactions. |
| Log Archive | optional | Preservation of transaction logs, in order to be able to get further back in time regarding transactions. |
| Traffic Encryption | optional | When data is exchanged over unsecured data transport facilities, it might be a good measure to encrypt the data at engine level. |
| Transaction Caching | optional | Retaining and keeping available of frequent issued transactions/queries, in order to improve performance. |
| Transaction Replication | optional | Multiplying transactions over multiple database instances, to maintain exact copies on data engine level. Mostly this is done to create a higher availability |
| Table Replication | optional | Multiplying tables over multiple database instances, to create an exact copy of a database on data engine level. This can be done to create a new development/test environment or to start creating a higher availability |
| File Export | optional | Extraction of data from the database and putting this in a file. This is used to execute a bulk data transfer from one instance to another. It can be used to create a replica or to import a dataset from one database into the other (ETL). Because it does not require a connection between Data Engines, it offers more flexibility and security, compared to direct Data Engine interaction. In both cases, the proper interfaces should be available. |
| File Import | optional | Loading of data from a file, to store this data in a database. This is used to restore a database from a replica or to import a large dataset from another database (ETL). Because it does not require a connection between Data Engines, it offers more flexibility and security, compared to direct Data Engine interaction. In both cases, the proper interfaces should be available. |
| Data Concealment | optional | Hiding of (privacy-sensitive) data objects when presenting/transferring/exporting data, by means of masking or scrambling. |
| Table Tiering | optional | Making use of different storage tiers for table retention, to reduce costs. |
| Table Encryption | optional | Encrypting (making unreadable without a key) of data when stored in a structured data store. |
| Platform Controlling | recommended | Administrative interface to configure and manage database systems. |
| Platform Logging | recommended | Keeping track of events, activities, interactions that occur during database system operation. |
